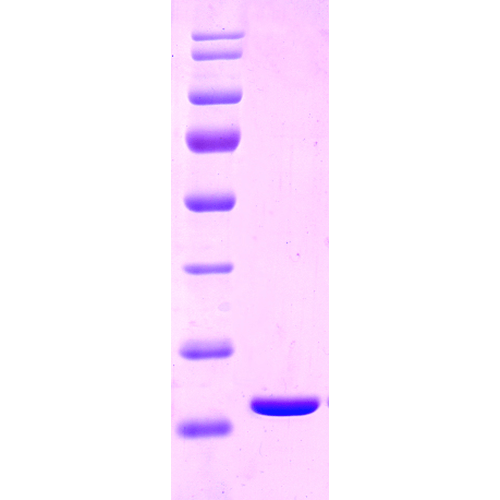
SPR-105A SPR-118A SPR-105B SPR-118B
Scientist.com Supplier
HSP27 Protein
Stressmarq Biosciences
DESCRIPTION
Human Recombinant HSP27 Protein
DETAILS
- Nature: Recombinant
- Purity: >90%
- Target: HSP27
- Category: Protein
- Conjugate: His tag
- References: 1. Kim K.K., Kim R., and Kim, S. (1998) Nature 394(6693): 595-599. 2. Van Montfort R., Slingsby C., and Vierling E. (2001) Addv Protein Chem. 59: 105-56. 3. Ehrnsperger M., Graber S., Gaestel M. and Buchner J. (1997) EMBO J. 16: 221-229. 4. Ciocca D.R., Oesterreich S., Chamness G.C., McGuire W.L., and Fugua S.A. (1993) J Natl Cancer Inst. 85 (19): 1558-70. 5. Sarto C. Binnz P.A. and Mocarelli P. (2000) Electrophoresis. 21(6): 1218-26. 6. Arrigo A.P. (2005) J Cell Biochem. 94(2): 241-6.
- Applications: WB | SDS-PAGE | Functional Assay | ELISA
- Field of Use: Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For research use only.
- Protein Size: ~27 kDa
- Purification: Affinity Purified
- Concentration: Lot/batch specific. See included datasheet.
- Research Areas: Cell Signaling | Protein Trafficking | Chaperone Proteins | Cell Signaling | Cytoskeleton | Microfilaments | Actin | Actin Assembly | Cell Signaling | Cytoskeleton | Microtubules | Cancer | Tumor Biomarkers | Cardiovascular System | Atherosclerosis | Cardiovascular System | Heart | Contractility
- Storage Buffer: 50mM Tris/HCl, pH8, 0.3M NaCl
- Alternative Names: 28kDa heat shock Protein, CMT2F Protein, HSP25 Protein, HSP27 Protein, HSP28 Protein, HSPB1 Protein, SRP27 Protein
- Cite This Product: Human Recombinant HSP27 Protein (StressMarq Biosciences, Canada, Cat # SPR-105A)
- Expression System: E. coli
- Species Full Name: Human
- Storage Temperature: -20ºC
- Shipping Temperature: Blue Ice or 4ºC
- Cellular Localization: Cytoplasm | Nucleus
- Scientific Background: HSP27s belong to an abundant and ubiquitous family of small heat shock proteins (sHSP). It is an important HSP found in both normal human cells and cancer cells. The basic structure of most sHSPs is a homologous and highly conserved amino acid sequence, with an α-crystallin-domain at the C-terminus and the WD/EPF domain at the less conserved N-terminus. This N-terminus is essential for the development of high molecular oligomers (1, 2). HSP27-oligomers consist of stable dimers formed by as many as 8-40 HSP27 protein monomers (3). The oligomerization status is connected with the chaperone activity: aggregates of large oligomers have high chaperone activity, whereas dimers have no chaperone activity (4). HSP27 is localized to the cytoplasm of unstressed cells but can redistribute to the nucleus in response to stress, where it may function to stabilize DNA and/or the nuclear membrane. Other functions include chaperone activity (as mentioned above), thermo tolerance in vivo, inhibition of apoptosis, and signal transduction. Specifically, in vitro, it acts as an ATP-independent chaperone by inhibiting protein aggregation and by stabilizing partially denatured proteins, which ensures refolding of the HSP70 complex. HSP27 is also involved in the apoptotic signaling pathway because it interferes with the activation of cytochrome c/Apaf-1/dATP complex, thereby inhibiting the activation of procaspase-9. It is also hypothesized that HSP27 may serve some role in cross-bridge formation between actin and myosin (5). And finally, HSP27 is also thought to be involved in the process of cell differentiation. The up-regulation of HSP27 correlates with the rate of phosphorylation and with an increase of large oligomers. It is possible that HSP27 may play a crucial role in termination of growth (6). Looking for more information on HSP27? Visit our new HSP27 Scientific Resource Guide at http://www.HSP27.com.
- Certificate of Analysis: This product has been certified >90% pure using SDS-PAGE analysis.
Equivalent Items
| ... Loading