SPR-325B SPR-325C SPR-325E
Alpha Synuclein A53T Mutant Monomers (Type 1)
Stressmarq Biosciences
Image
Image
DESCRIPTION
Human Recombinant A53T Mutant Alpha Synuclein Protein Monomers (Type 1)
DETAILS
- Nature: Recombinant
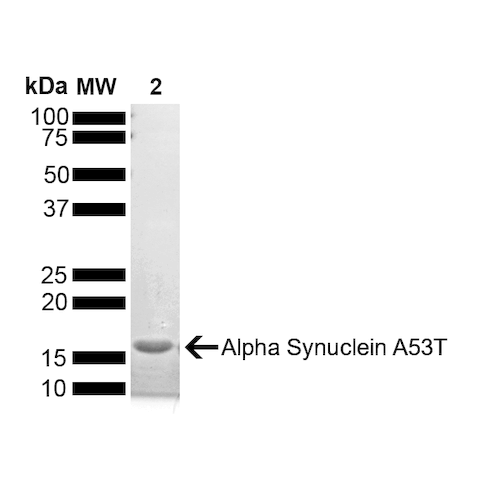
- Purity: >95%
- Target: Alpha Synuclein A53T Mutant
- Category: Protein
- Conjugate: No tag
- References: 1. “Genetics Home Reference: SNCA”. US National Library of Medicine. (2013). 2. Zhang L., et al. (2008) Brain Res. 1244: 40-52. 3. Alim M.A., et al. (2002) J Biol Chem. 277(3): 2112-2117. 4. Kokhan V.S., Afanasyeva M.A., Van'kin G. (2012) Behav. Brain. Res. 231(1): 226-230. 5. Spillantini M.G., et al. (1997) Nature. 388(6645): 839-840. 6. Mezey E., et al. (1998) Nat Med. 4(7): 755-757. 7. Polymeropoulos, M. H. (1998). Science. 276(5321), 2045–2047 8. Conway, K.E., et al. (1998). Nat Med. 4(11):1318-20
- Applications: WB | SDS-PAGE | In vivo assay | In vitro assay
- Field of Use: Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For research use only.
- Protein Size: ~14.46 kDa
- Purification: Ion-exchange Purified
- Concentration: Lot/batch specific. See included datasheet.
- Protein Length: Full Length
- Research Areas: Neuroscience | Neurodegeneration | Alzheimer's Disease | Tangles & Tau | Neuroscience | Neurodegeneration | Parkinson's Disease | Synuclein | Neuroscience | Neurodegeneration | Multiple System Atrophy
- Storage Buffer: PBS pH 7.4
- Alternative Names: A53T mutant alpha synuclein, A53T mutated SNCA, A53T Alpha synuclein monomer, Ala53thr mutant alpha synuclein, Alpha synuclein protein, Alpha-synuclein protein, Non-A beta component of AD amyloid protein, Non-A4 component of amyloid precursor protein, NACP protein, SNCA protein, NACP protein, PARK1 protein, Alpha synuclein monomers, SYN protein, Parkinson disease familial 1 Protein
- Cite This Product: Human Recombinant A53T Alpha Synuclein Protein Monomer (StressMarq Biosciences Inc., Victoria BC CANADA, Catalog # SPR-325B)
- Expression System: E. coli
- Species Full Name: Human
- Amino Acid Sequence: MDVFMKGLSK AKEGVVAAAE KTKQGVAEAA GKTKEGVLYV GSKTKEGVVH GVTTVAEKTK EQVTNVGGAV VTGVTAVAQK TVEGAGSIAA ATGFVKKDQL GKNEEGAPQE GILEDMPVDP DNEAYEMPSE EGYQDYEPEA
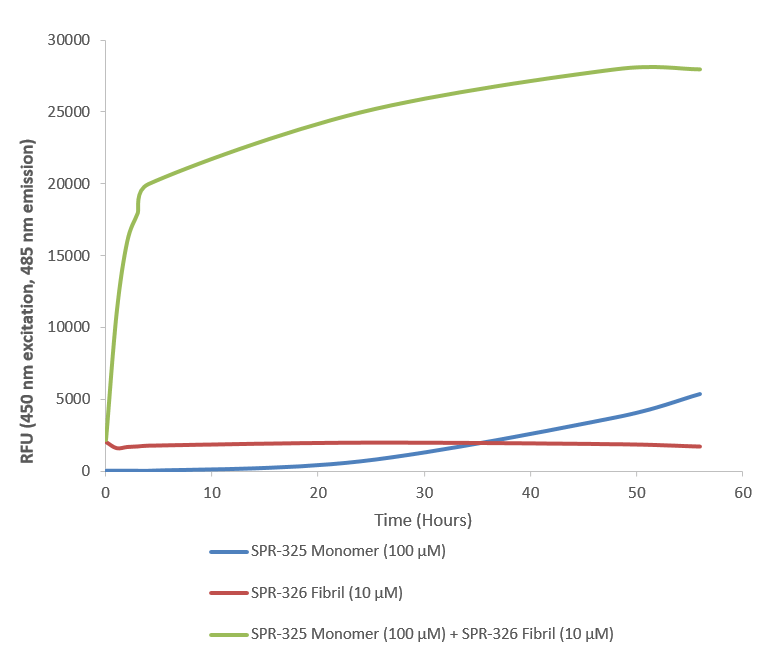
- Biological Activity: 100 µM A53T alpha synuclein protein monomer (SPR-325) seeded with 10 uM A53T alpha synuclein protein PFF (SPR-326) in 25 µM Thioflavin T (PBS pH 7.4, 100 µl reaction volume) generated a fluorescence intensity of 28 000 Relative Fluorescence Units after incubation at 37°C with shaking at 600 rpm for 56 hours. Fluorescence was measured by excitation at 450 nm and emission at 485 nm on a Molecular Devices Gemini XPS microplate reader.
- Storage Temperature: -80ºC
- Shipping Temperature: Dry Ice. Shipping note: Product will be shipped separately from other products purchased in the same order.
- Cellular Localization: Cytoplasm | Membrane | Nucleus
- Scientific Background: Alpha-Synuclein (SNCA) is expressed predominantly in the brain, where it is concentrated in presynaptic nerve terminals (1). Alpha-synuclein is highly expressed in the mitochondria of the olfactory bulb, hippocampus, striatum and thalamus (2). Functionally, it has been shown to significantly interact with tubulin (3), and may serve as a potential microtubule-associated protein. It has also been found to be essential for normal development of the cognitive functions; inactivation may lead to impaired spatial learning and working memory (4). SNCA fibrillar aggregates represent the major non A-beta component of Alzheimers disease amyloid plaque, and a major component of Lewy body inclusions, and Parkinson's disease. Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the progressive accumulation in selected neurons of protein inclusions containing alpha-synuclein and ubiquitin (5, 6). The A53T mutation is a missense point mutation where alanine is replaced by threonine at the 53rd amino acid. This mutation has been linked to early-onset Parkinson's Disease and increased rates of alpha synuclein fibrillization.
- Certificate of Analysis: Certified >95% pure using SDS-PAGE analysis.